Table of Contents
What is Market and How Market Works?
In general, a market refers to a system or mechanism that allows buyers and sellers to exchange goods and services. It is a place where buyers and sellers come together to carry out transactions. The key feature of a market is the interaction between buyers and sellers to establish a price for a particular good or service.
Markets can be physical or virtual. Physical markets are the traditional marketplaces where buyers and sellers meet face-to-face to exchange goods and services. For example, farmers’ markets or fish markets. Virtual markets, on the other hand, refer to online platforms that allow buyers and sellers to trade goods and services over the internet.
A market works through the forces of supply and demand. When a good or service is in high demand, its price tends to rise as buyers compete for limited supply. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, the price tends to fall as sellers compete to find buyers. The intersection of supply and demand curves determines the market price of a good or service.
The market also involves the roles of buyers and sellers. Sellers offer products or services for sale, while buyers decide whether or not to purchase them based on their needs, preferences, and budget. In a competitive market, sellers compete with each other to offer the best prices, quality, and customer service to attract buyers.
Overall, markets play a crucial role in the economy, as they help allocate resources efficiently and provide a mechanism for businesses to generate revenue and consumers to acquire the goods and services they need.
Structure of Market
Resource Market – Manufacturers – Intermediary Markets – Retailer – Govt.
(Check out below image to understand more)(Know more below with Description)
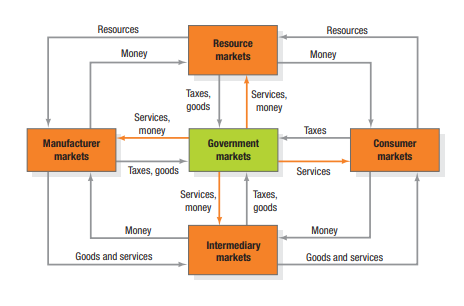
What is Resources Market
A resources market is a market in which natural resources, such as commodities, energy, and minerals, are traded. These resources are essential inputs for many industries and are therefore subject to global supply and demand dynamics.
The resources market is often divided into different categories, including:
1. Commodity market: The commodity market deals with raw materials that are used in the production of goods and services, such as agricultural products, metals, and energy.
2. Energy market: The energy market deals with the production, trading, and distribution of energy, including oil, natural gas, coal, and renewable energy.
3. Mineral market: The mineral market deals with minerals that are used in the production of goods, such as copper, iron, and gold.
The resources market is an important part of the global economy, and the prices of resources can have a significant impact on industries and economies around the world. Many businesses and investors participate in the resources market to manage risks, generate profits, and secure access to essential resources.
Who are Manufacturers
Manufacturers are businesses that produce and sell goods or products for use or consumption by individuals or other businesses. They are a vital part of the global economy, providing jobs, generating revenue, and producing a wide range of goods and services.
Manufacturers are involved in every stage of the production process, from the acquisition of raw materials to the assembly and distribution of finished products. They may use a variety of production methods and technologies, from manual labor to highly automated manufacturing systems, depending on the type of product being produced.
Manufacturers may specialize in the production of specific types of goods, such as automobiles, electronics, clothing, or food products. Some manufacturers produce intermediate goods or components that are used by other manufacturers to produce final products.
Manufacturers must compete with other businesses in their industry to attract customers and generate revenue. They must continually innovate and improve their products and production processes to stay competitive. They must also manage their supply chain effectively to ensure a steady supply of raw materials and minimize production costs.
Overall, manufacturers play a crucial role in the economy, producing goods and services that meet the needs of individuals and businesses around the world. They contribute to economic growth, job creation, and technological innovation, making them a key driver of progress and prosperity.
What is Intermediate Market ?
The intermediate market, also known as the business-to-business (B2B) market, refers to the trade of goods and services between businesses, rather than between businesses and individual consumers. In this market, the goods and services produced by one business are sold to another business, which then uses them in the production of their own goods or services.
The intermediate market involves a complex system of relationships between businesses, including suppliers, manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers. These businesses may be involved in the production of raw materials, the manufacturing of intermediate goods, or the provision of services that are necessary for other businesses to operate.
For example, a manufacturer of electronic goods may purchase components, such as circuit boards, from a supplier, who in turn may purchase raw materials, such as copper and plastics, from other businesses. The manufacturer may then sell the finished goods to a distributor, who supplies them to retailers for sale to individual consumers.
Who is Retailers ?
Retailers are businesses that sell goods or services to individual consumers for personal or household use. They are an important part of the global economy, providing jobs, generating revenue, and offering a wide range of products and services to meet the needs and wants of consumers.
Retailers operate in a variety of formats, including physical stores, online stores, and a combination of both. They may specialize in a particular product category, such as electronics, clothing, or food, or they may offer a wide range of products across multiple categories.
Retailers are responsible for managing their inventory, merchandising their products, and attracting customers to their stores or websites. They must compete with other retailers to offer the best prices, selection, and customer experience in order to attract and retain customers.
Retailers may purchase their products directly from manufacturers or wholesalers, or they may work with intermediaries, such as distributors or agents, to source their products. They may also offer additional services, such as financing, installation, or repair, to enhance the customer experience.
Overall, retailers play a crucial role in the economy, providing a key link between manufacturers and consumers. They help to stimulate consumer demand, support employment, and drive economic growth, making them a vital component of the business ecosystem.

